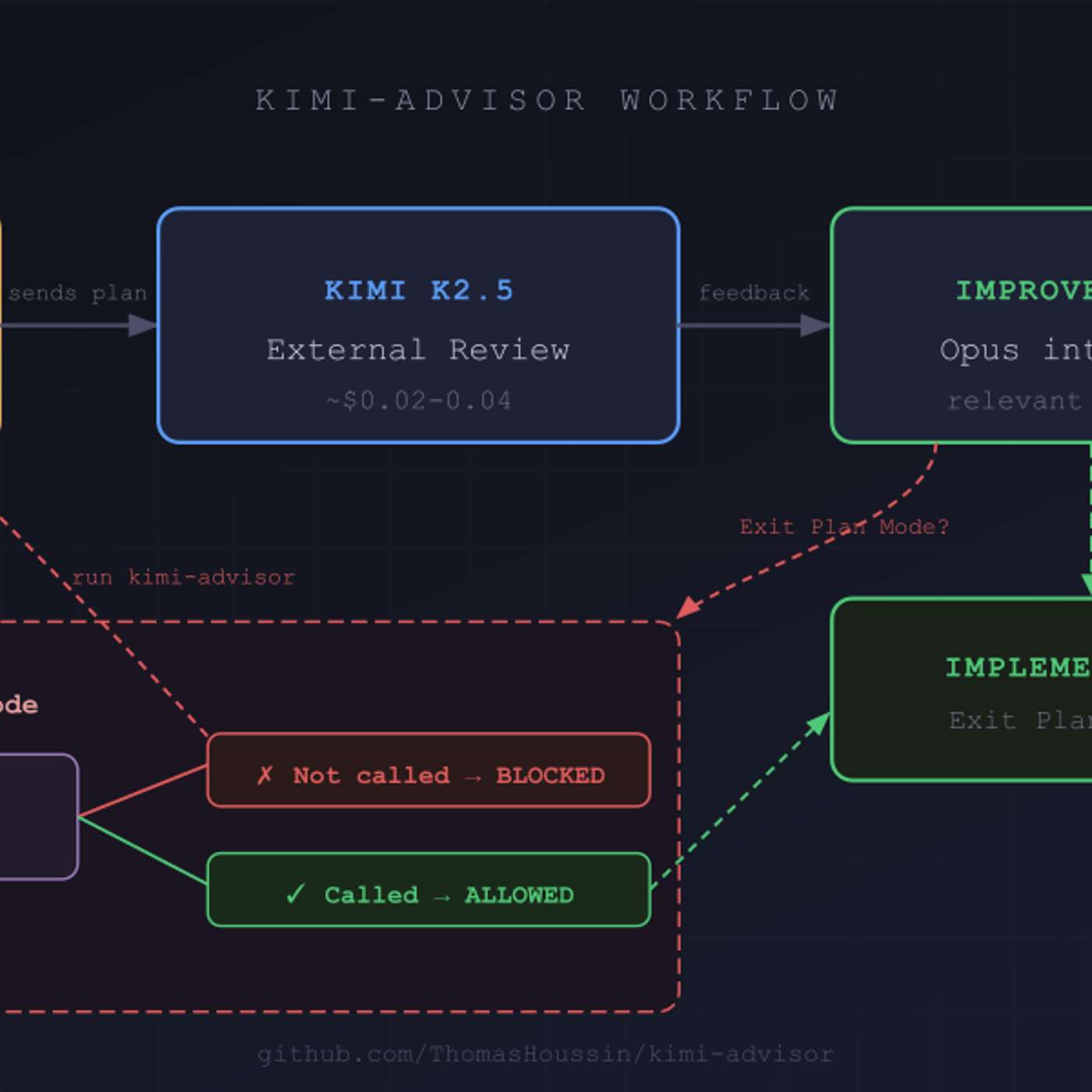
To improve code quality, use a secondary AI model from a different provider (e.g., Moonshot AI's Kimi) to review plans generated by a primary model (e.g., Anthropic's Claude). This introduces cognitive diversity and avoids the shared biases inherent in a single model family, leading to a more robust and enriching review process.
Related Insights
An effective AI development workflow involves treating models as a team of specialists. Use Claude as the reliable 'workhorse' for building an application from the ground up, while leveraging models like Gemini or GPT-4 as 'advisory models' for creative input and alternative problem-solving perspectives.
Relying on a single model family for generation and review is suboptimal. Blitzy found that using models from different developers (e.g., OpenAI, Anthropic) to check each other's work produces tremendously better results, as each family has distinct strengths and reasoning patterns.
LLMs often get stuck or pursue incorrect paths on complex tasks. "Plan mode" forces Claude Code to present its step-by-step checklist for your approval before it starts editing files. This allows you to correct its logic and assumptions upfront, ensuring the final output aligns with your intent and saving time.
To overcome the challenge of reviewing AI-generated code, have different LLMs like Claude and Codex review the code. Then, use a "peer review" prompt that forces the primary LLM to defend its choices or fix the issues raised by its "peers." This adversarial process catches more bugs and improves overall code quality.
Prompting a different LLM model to review code generated by the first one provides a powerful, non-defensive critique. This "second opinion" can rapidly identify architectural issues, bugs, and alternative approaches without the human ego involved in traditional code reviews.
To improve the quality and accuracy of an AI agent's output, spawn multiple sub-agents with competing or adversarial roles. For example, a code review agent finds bugs, while several "auditor" agents check for false positives, resulting in a more reliable final analysis.
The comparison reveals that different AI models excel at specific tasks. Opus 4.5 is a strong front-end designer, while Codex 5.1 might be better for back-end logic. The optimal workflow involves "model switching"—assigning the right AI to the right part of the development process.
Rather than relying on a single AI, an agentic system should use multiple, different AI models (e.g., auditor, tester, coder). By forcing these independent agents to agree, the system can catch malicious or erroneous behavior from a single misaligned model.
Define different agents (e.g., Designer, Engineer, Executive) with unique instructions and perspectives, then task them with reviewing a document in parallel. This generates diverse, structured feedback that mimics a real-world team review, surfacing potential issues from multiple viewpoints simultaneously.
To prevent AI coding assistants from hallucinating, developer Terry Lynn uses a two-step process. First, an AI generates a Product Requirements Document (PRD). Then, a separate AI "reviewer" rates the PRD's clarity out of 10, identifying gaps before any code is written, ensuring a higher rate of successful execution.