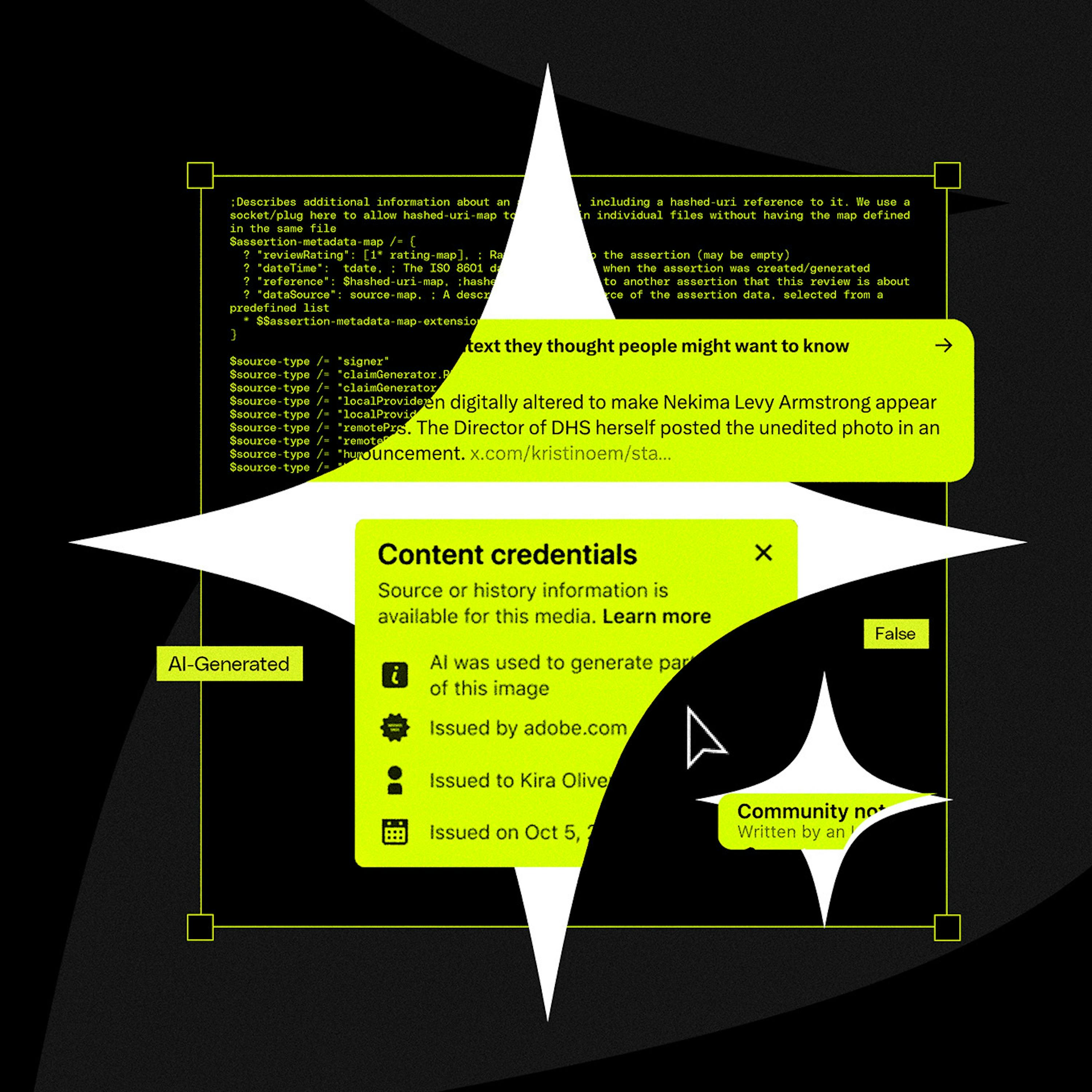
A critical failure point for C2PA is that social media platforms themselves can inadvertently strip the crucial metadata during their standard image and video processing pipelines. This technical flaw breaks the chain of provenance before the content is even displayed to users.
Related Insights
As AI makes it easy to fake video and audio, blockchain's immutable and decentralized ledger offers a solution. Creators can 'mint' their original content, creating a verifiable record of authenticity that nobody—not even governments or corporations—can alter.
Adam Mosseri’s public statement that we can no longer assume photos or videos are real marks a pivotal shift. He suggests moving from a default of trust to a default of skepticism, effectively admitting platforms have lost the war on deepfakes and placing the burden of verification on users.
Major tech companies publicly champion their support for the C2PA standard to appear proactive about the deepfake problem. However, this support is often superficial, serving as a "meritless badge" or PR move while they avoid the hard work of robust implementation and ecosystem-wide collaboration.
Beyond data privacy, a key ethical responsibility for marketers using AI is ensuring content integrity. This means using platforms that provide a verifiable trail for every asset, check for originality, and offer AI-assisted verification for factual accuracy. This protects the brand, ensures content is original, and builds customer trust.
The C2PA standard's effectiveness depends on a complete ecosystem of participation, from capture (cameras) to distribution (platforms). The refusal of major players like Apple and X to join creates fatal gaps, rendering the entire system ineffective and preventing a network effect.
Politician Alex Boris argues that expecting humans to spot increasingly sophisticated deepfakes is a losing battle. The real solution is a universal metadata standard (like C2PA) that cryptographically proves if content is real or AI-generated, making unverified content inherently suspect, much like an unsecure HTTP website today.
While camera brands like Sony and Nikon support C2PA on new models, the standard's adoption is crippled by the inability to update firmware on millions of existing professional cameras. This means the vast majority of photos taken will lack provenance data for years, undermining the entire system.
The rise of convincing AI-generated deepfakes will soon make video and audio evidence unreliable. The solution will be the blockchain, a decentralized, unalterable ledger. Content will be "minted" on-chain to provide a verifiable, timestamped record of authenticity that no single entity can control or manipulate.
The shift from "Copyright" to "Content Detection" in YouTube Studio is a strategic response to AI. The platform is moving beyond protecting just video assets to safeguarding a creator's entire digital identity—their face and voice. This preemptively addresses the rising threat of deepfakes and unauthorized AI-generated content.
C2PA was designed to track a file's provenance (creation, edits), not specifically to detect AI. This fundamental mismatch in purpose is why it's an ineffective solution for the current deepfake crisis, as it wasn't built to be a simple binary validator of reality.