The release of Gemini 3.1 Pro highlights a market shift where raw capability is becoming table stakes. Google achieved a massive intelligence jump with zero incremental cost, demonstrating that the new competitive frontier for AI models is commoditizing intelligence and winning on distribution and price efficiency, rather than just holding the top spot on a benchmark for a few weeks.
Related Insights
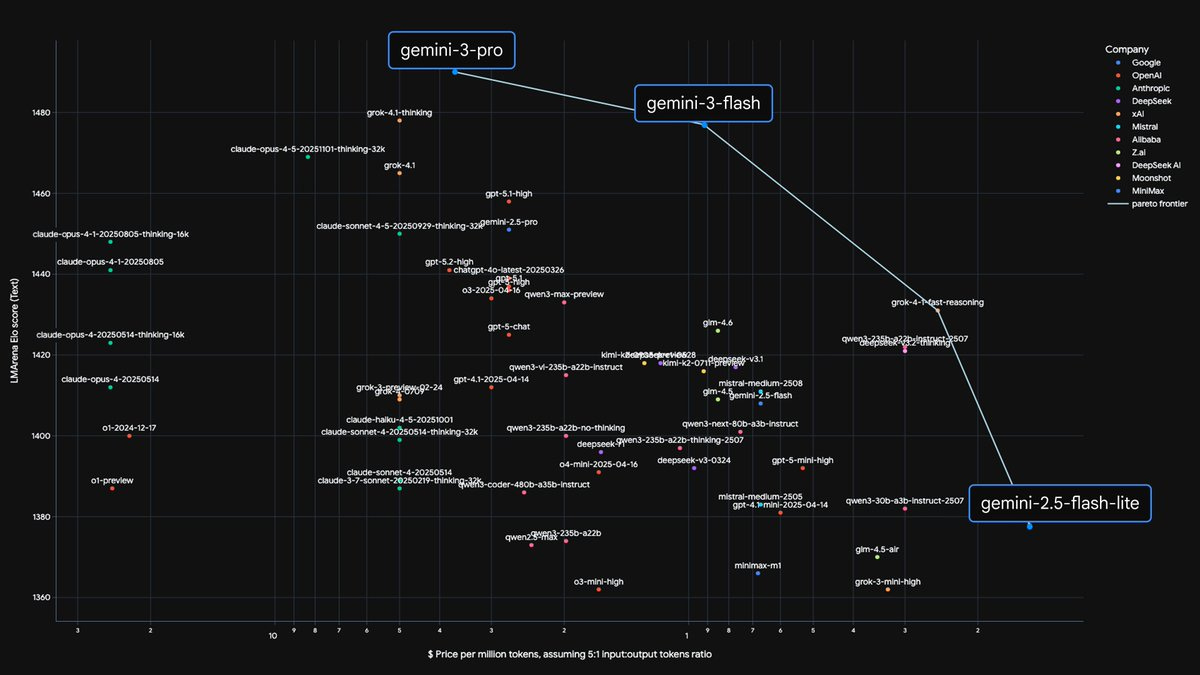
The primary threat from competitors like Google may not be a superior model, but a more cost-efficient one. Google's Gemini 3 Flash offers "frontier-level intelligence" at a fraction of the cost. This shifts the competitive battleground from pure performance to price-performance, potentially undermining business models built on expensive, large-scale compute.
Models like Gemini 3 Flash show a key trend: making frontier intelligence faster, cheaper, and more efficient. The trajectory is for today's state-of-the-art models to become 10x cheaper within a year, enabling widespread, low-latency, and on-device deployment.
Google successfully trained its top model, Gemini 3 Pro, on its own TPUs, proving a viable alternative to NVIDIA's chips. However, because Google doesn't sell these TPUs, NVIDIA retains its monopoly pricing power over every other company in the market.
Google can afford to offer its LLM for free, creating immense pricing pressure on competitors like OpenAI. This strategy aims to eliminate competition by making their business models unprofitable, securing a monopoly for Google before it begins to monetize.
Google's Gemini models show that a company can recover from a late start to achieve technical parity, or even superiority, in AI. However, this comeback highlights that the real challenge is translating technological prowess into product market share and user adoption, where it still lags.
The cost for a given level of AI capability has decreased by a factor of 100 in just one year. This radical deflation in the price of intelligence requires a complete rethinking of business models and future strategies, as intelligence becomes an abundant, cheap commodity.
Google's strategy involves creating both cutting-edge models (Pro/Ultra) and efficient ones (Flash). The key is using distillation to transfer capabilities from large models to smaller, faster versions, allowing them to serve a wide range of use cases from complex reasoning to everyday applications.
OpenAI is now reacting to Google's advancements with Gemini 3, a complete reversal from three years ago. Google's strengths in infrastructure, proprietary chips, data, and financial stability are giving it a significant competitive edge, forcing OpenAI to delay initiatives and refocus on its core ChatGPT product.
The narrative of endless demand for NVIDIA's high-end GPUs is flawed. It will be cracked by two forces: the shift of AI inference to on-device flash memory, reducing cloud reliance, and Google's ability to give away its increasingly powerful Gemini AI for free, undercutting the revenue models that fuel GPU demand.
While competitors like OpenAI must buy GPUs from NVIDIA, Google trains its frontier AI models (like Gemini) on its own custom Tensor Processing Units (TPUs). This vertical integration gives Google a significant, often overlooked, strategic advantage in cost, efficiency, and long-term innovation in the AI race.