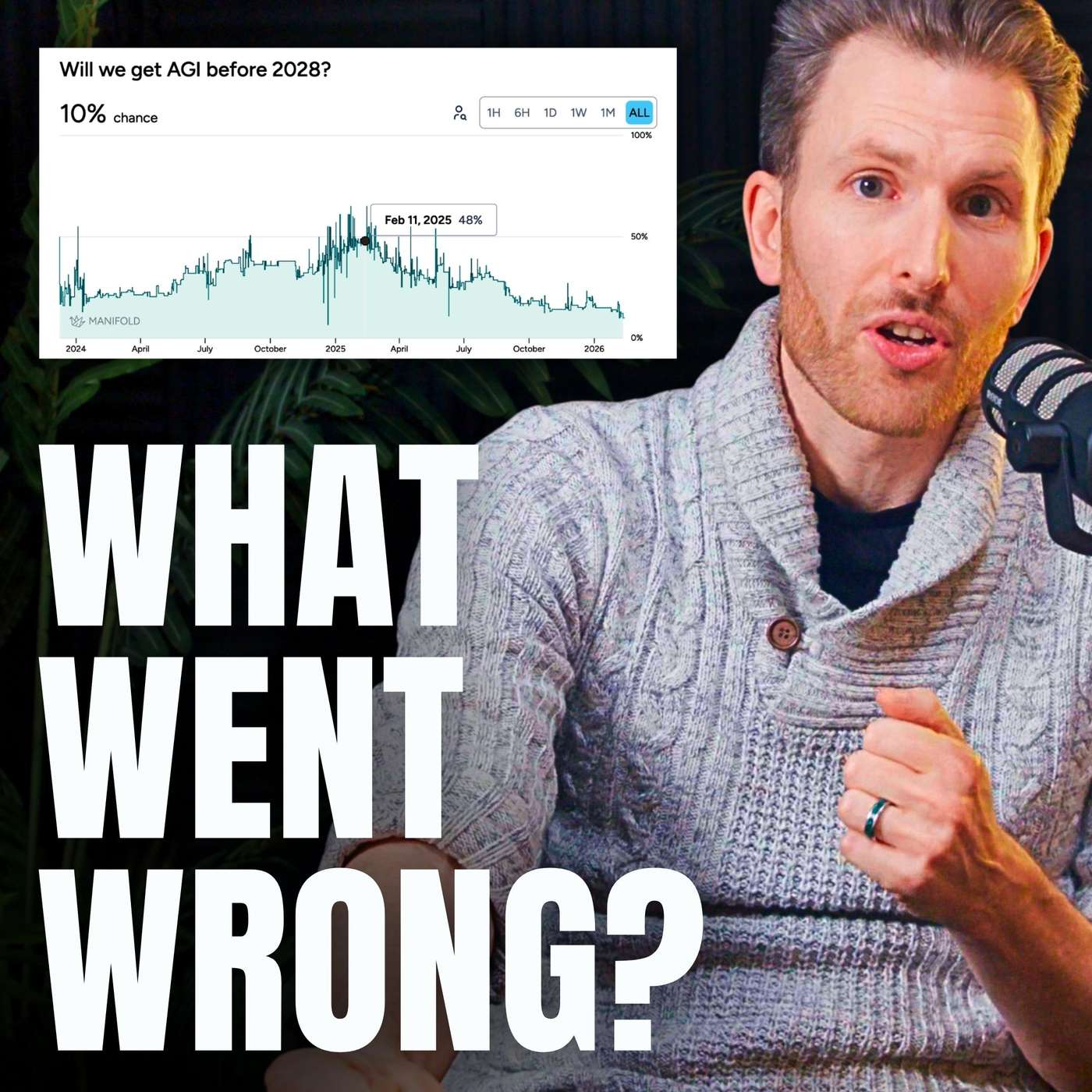
A growing gap exists between AI's performance in demos and its actual impact on productivity. As podcaster Dwarkesh Patel noted, AI models improve at the rapid rate short-term optimists predict, but only become useful at the slower rate long-term skeptics predict, explaining widespread disillusionment.
Related Insights
Many AI implementation projects are being paused or canceled due to a lack of immediate ROI. This reflects Amara's Law: we overestimate technology in the short term and underestimate it long term. Leaders must treat AI as a long-term strategic investment, not a short-term magic bullet.
The argument that AI adoption is slow due to normal tech diffusion is flawed. If AI models possessed true human-equivalent capabilities, they would be adopted faster than human employees because they could onboard instantly and eliminate hiring risks. The current lack of widespread economic value is direct evidence that today's AI models are not yet capable enough for broad deployment.
There's a significant gap between AI performance on structured benchmarks and its real-world utility. A randomized controlled trial (RCT) found that open-source software developers were actually slowed down by 20% when using AI assistants, despite being miscalibrated to believe the tools were helping. This highlights the limitations of current evaluation methods.
Many developers dismiss AI coding tools as a fad based on experiences with earlier, less capable versions. The rapid, non-linear progress means perceptions become dated in months, creating a massive capability gap between what skeptics believe and what current tools can actually do.
Users frequently write off an AI's ability to perform a task after a single failure. However, with models improving dramatically every few months, what was impossible yesterday may be trivial today. This "capability blindness" prevents users from unlocking new value.
A critique from a SaaS entrepreneur outside the AI hype bubble suggests that current tools often just accelerate the creation of corporate fluff, like generating a 50-slide deck for a five-minute meeting. This raises questions about whether AI is creating true productivity gains or just more unnecessary work.
Human intuition is a poor gauge of AI's actual productivity benefits. A study found developers felt significantly sped up by AI coding tools even when objective measurements showed no speed increase. The real value may come from enabling tasks that otherwise wouldn't be attempted, rather than simply accelerating existing workflows.
Despite significant promotion from major vendors, AI agents are largely failing in practical enterprise settings. Companies are struggling to structure them properly or find valuable use cases, creating a wide chasm between marketing promises and real-world utility, making it the disappointment of the year.
A paradox of rapid AI progress is the widening "expectation gap." As users become accustomed to AI's power, their expectations for its capabilities grow even faster than the technology itself. This leads to a persistent feeling of frustration, even though the tools are objectively better than they were a year ago.
While spending on AI infrastructure has exceeded expectations, the development and adoption of enterprise-level AI applications have significantly lagged. Progress is visible, but it's far behind where analysts predicted it would be, creating a disconnect between the foundational layer and end-user value.